Familial Retinoblastoma Involves the Transmission of What From Parent to Offspring?
Untreated retinoblastoma can exist fatal; in developed countries, advances in treatment have resulted in a 95 to 99% survival rate.
What are the Types of Retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma occurs in 2 forms � a heritable and a non-heritable (sporadic) form. Heritable retinoblastoma indicates that the tendency to develop retinoblastoma is transmitted from parents to offspring, and accounts for 40% of the cases. The differences between the two forms are listed below:
Children with the heritable type of retinoblastoma are more at chance of developing cancer (second non-ocular cancers) in other organs of the body, the about common of which are osteogenic sarcoma (bone cancer), soft tissue sarcomas and melanomas (tumors of pigmentary cells). These second cancers are more common in patients who have received radiotherapy for their retinoblastoma, and even more than so when this radiations has been given earlier 12 months of age. These 2d primary malignancies are the most mutual cause of death following retinoblastoma in developed countries.
Why does Retinoblastoma occur?
The development of most cases of retinoblastoma may be explained by Knudson�s ii hit hypothesis.
Every private has 23 pairs of chromosomes, i chromosome of every pair obtained from each parent. Genes (containing codes to synthesize proteins and thus determining various characteristics of an individual) are situated on these chromosomes. The retinoblastoma cistron (or RB1) is situated on the 14th band of the long arm of chromosome 13 (13q14). This is a tumor suppressor gene. This ways that presence of this factor in its normal form protects against retinoblastoma.
Co-ordinate to Knudson�southward two striking hypothesis, the DNA has to endure �two hits� or ii mutations for the cancer to occur.
In the heritable type of retinoblastoma, ane mutation is inherited from the parent, and and then all the cells in the trunk have this mutation (germline mutation). The second mutation occurs afterward after fertilization in the retinal cells, resulting in retinoblastoma (somatic mutation). In the sporadic diverseness, both mutations occur inside a single retinal cell afterward fertilisation of the egg (both are somatic mutations).
Recently, another variety of retinoblastoma has been discovered, where the retinoblastoma gene was normal, just there was a loftier level of amplification of the MYCN gene only in the tumor cells. This does non result in heritable retinoblastoma, and these children practise non take any of the characteristics of heritable retinoblastoma, including the risk of transmission to offspring.
What are the Symptoms of Retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma may present in a variety of ways. Still, the virtually mutual modes of presentation are -
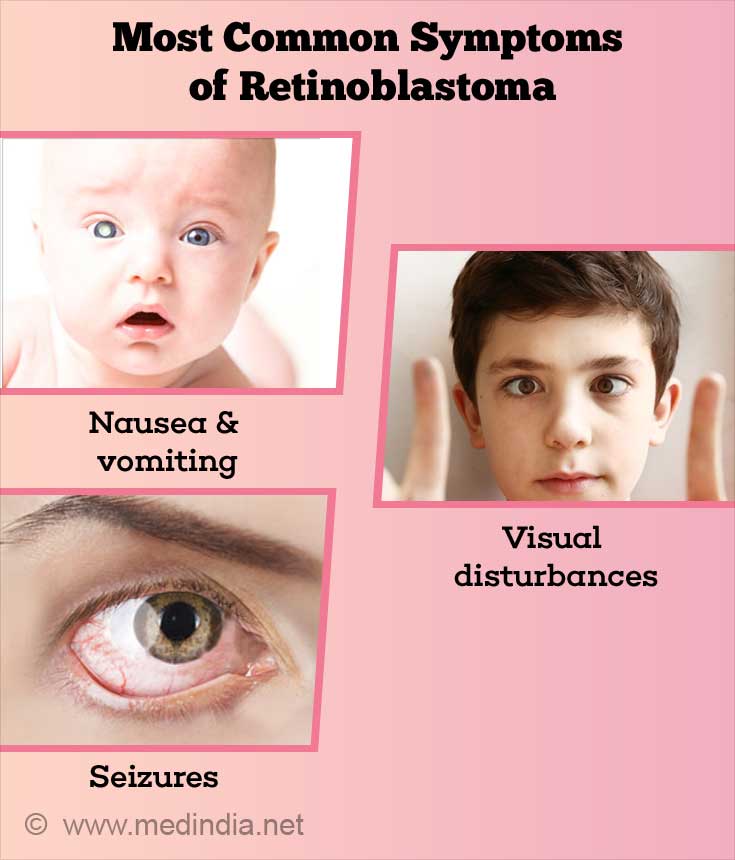
Less common modes of presentation include blood in the anterior bedchamber (seen behind the cornea), cataract, increased pressure in the eye and inflammation of the tissues surrounding the eye. In neglected cases, spread exterior the eyeball results in the middle being pushed forrad (proptosis) and appearing very prominent.
Retinoblastoma most unremarkably spreads along the optic nervus and into the brain and skull bones. It spreads through the blood to the bone marrow. Other organs to which it can spread are bones of the arms and legs, spinal cord, lymph nodes and abdominal organs.
How do y'all Diagnose and Evaluate a Child with Retinoblastoma?
- The diagnosis of retinoblastoma is mainly clinical. The classical presentation of leucocoria or whitish advent of the student should be considered to be retinoblastoma unless proved otherwise. The student is dilated and a detailed fundus (examination of the retina) is carried out, to determine if the tumor is monofocal or multifocal. If multifocal, all the tumors should be documented. Since virtually children in this age group are not very cooperative, an exam under anesthesia is required in all patients for a thorough cess of ocular illness prior to treatment.
- Ultrasonography (ultrasound exam of the center and orbit) measures the tumor size and shows the presence of heterogeneity (variations in the tumor) and calcification (aggregating of calcium in tissues)
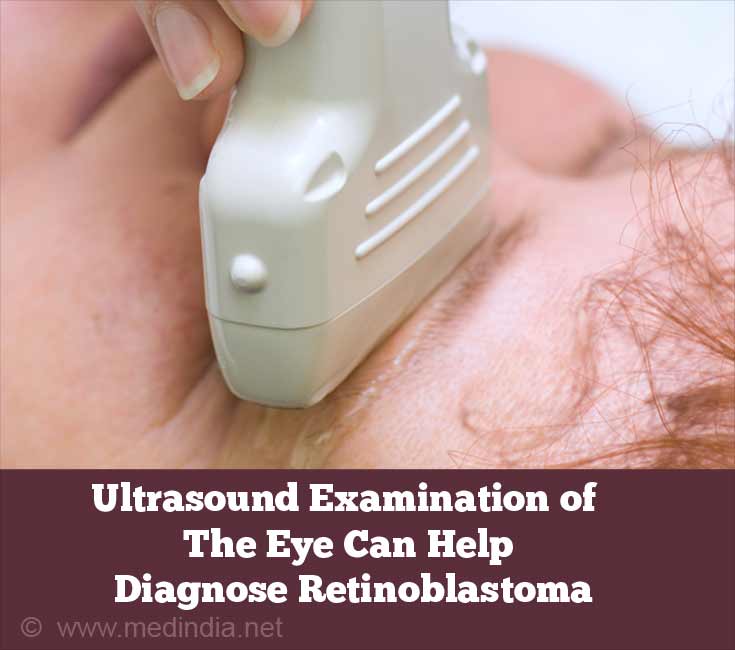
- CT (computed tomography) browse of the centre may show calcification. However, CT scan is less preferred because it exposes the child to radiation.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the heart, orbit and head is the preferred manner of imaging to evaluate the tumor in the eye and to detect possible extension into the orbit and brain. MRI can also observe if there an associated tumor of the pineal gland; this condition is referred to every bit trilateral retinoblastoma. MRI likewise helps in differentiating other conditions that simulate retinoblastoma.
- If extension into the optic nervus (the nerve at the back of the eye that transmits visual signals from the retina to the brain) is suspected, a lumbar puncture (placing a needle into the back and withdrawing cerebrospinal fluid which surrounds the spinal cord) may be washed.
- If at that place is evidence of extension outside the eye, os scans and bone marrow testing to detect the spread are required.
- Genetic studies to determine heritability and the type of genetic involvement are done to help in genetic counselling.
What are the Conditions that Simulate Retinoblastoma?
At that place are a number of weather condition that simulate retinoblastoma as they also cause leucocoria or a whitish appearance of the pupil. Though all of these atmospheric condition (collectively referred to as pseudoglioma) should be kept in mind and the patient must exist examined to rule out these conditions, leucocoria should be considered to exist due to retinoblastoma unless proved otherwise, equally this status can be fatal.
How do Y'all Treat Retinoblastoma?
The management of retinoblastoma involves a multidisciplinary approach and involves ophthalmologists, pediatric oncologists (doctors who specialise in cancer in children), pathologists, radiations oncologists (doctors who specialise in giving radiotherapy for cancers) and genetic counsellors. The principal focus of treatment in avant-garde disease is the preservation of life; however modern techniques have more precise goals like preservation of the eyeball and vision as far as possible.
The treatment of retinoblastoma involves strategically choosing among the various available modalities according to the individual case. This would depend on laterality, stage of the disease, age of the kid and presence of spread at the fourth dimension of diagnosis. In children who present with advanced disease contained in one middle with no visual potential in that eye, that center is surgically removed , resulting in a 95- 99% cure rate. Where at that place is visual potential or in bilateral tumors, chemotherapy (treatment with anti-cancer drugs) is the handling of choice. Chemotherapy is often used in conjunction with other modalities, especially in the concept of chemoreduction, wherein the size of the tumor is reduced with chemotherapy, thus rendering the tumor amenable to one of the local therapies.
The following table lists some of the important modalities of treating retinoblastoma.
What is the Prognosis (Outcome) of Retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma is fatal if untreated due to spread to the encephalon and various organs of the torso. Since early diagnosis and treatment is optimal in industrialised countries, the prognosis for the eyes is very good. The latest techniques of intra-arterial chemotherapy (referred to as ophthalmic artery chemosurgery or OAC) and intravitreal injections have reduced the need for removal of the optics, and for external beam irradiation. Nevertheless, long term outcomes still depend on the development of secondary tumors, predominantly os tumors. The take a chance of second tumors increases with radiation for the treatment of the original condition.
Developed survivors of retinoblastoma oft have subnormal visual function.
What is the Protocol for Patients With Successfully Treated Retinoblastoma?
Children with unilateral retinoblastoma without a germline mutation take a very pocket-sized hazard of developing a tumor in the other eye. A regular clinical eye examination and ultrasound examination is recommended.
With treated bilateral retinoblastoma, clinical examinations are conducted every iii-six months upwardly to the historic period of vii years, then annually, and subsequently every 2 years for life not only for new retinal tumors, merely also for other second non-ocular tumors.
Patients with heritable retinoblastoma should preferably avoid radiotherapy, tobacco and exposure to sunlight (agents that impairment Deoxyribonucleic acid and thus predispose to cancers) to reduce the adventure of second non-ocular tumors.
Individuals with retinomas (not-cancerous retinal tumors) should undergo clinical test and imaging every 1-two years to detect cancerous (malignant) alter.
Genetic Counselling
Genetic counselling forms an integral part of the direction of a patient with retinoblastoma. The susceptibility to heritable retinoblastoma is inherited in an autosomal ascendant manner. Unfortunately, genetic counselling is very complicated in retinoblastoma and depends on the type of retinoblastoma and genetic testing. The post-obit table gives the take a chance of having children with retinoblastoma, and the risk for subsequent children if one child develops the disease.
The in a higher place table is a simplified version, and bodily risks should exist determined after molecular genetic testing of the claret of at hazard persons.
How Practice You Foreclose Retinoblastoma?
- Retinoblastoma can simply be prevented by proper genetic counselling, wherein parents exercise non get in for more children if at that place is a loftier take a chance for developing retinoblastoma.

- Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis may be fabricated by testing the embryo after in-vitro fertilisation (test tube baby). If found to have the retinoblastoma gene mutation, then implantation may be deferred, thus preventing a pregnancy in which the child is at risk.
- Prenatal genetic testing (during pregnancy) may be done by chorionic villus sampling (cells from placenta) before 12 weeks of pregnancy, or from amniotic fluid (after 12 weeks of pregnancy). If found to be positive for the mutant gene, and then fetal ultrasound can exist used for early detection of tumors, and an early delivery may exist planned to beginning early treatment. Even so, non-continuation of pregnancy has certain medical and legal bug which demand to exist ascertained.
Screening of Family Members
- In the absence of a family unit history, the parents of a child with retinoblastoma should be examined for healed retinal scars or evidence of a retinoma (non-malignant form of retina tumor). These directly support the heritable form of retinoblastoma.
- Siblings of a child with retinoblastoma should undergo molecular genetic testing, and if constitute to accept a germline mutation, should undergo clinical examination every iii-4 weeks until the age of i twelvemonth, and every 3-iv months until the age of 5 years. Afterwards that, annual screening and clinical examination of the entire body should exist carried out for life.
- Any person with a retinoma should exist screened with eye examination https://world wide web.medindia.net/health-screening-test/routine-eye-test.htm About Routine Eye Examination and ultrasound every one or two years for life.
fragosobountiturill.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.medindia.net/patientinfo/retinoblastoma.htm
0 Response to "Familial Retinoblastoma Involves the Transmission of What From Parent to Offspring?"
Post a Comment